Learn More About Our Solution For Ulcerative Colitis
NX-13 Modulates Epithelial Integrity and Mucosal Immune Responses in the Gastrointestinal Tract
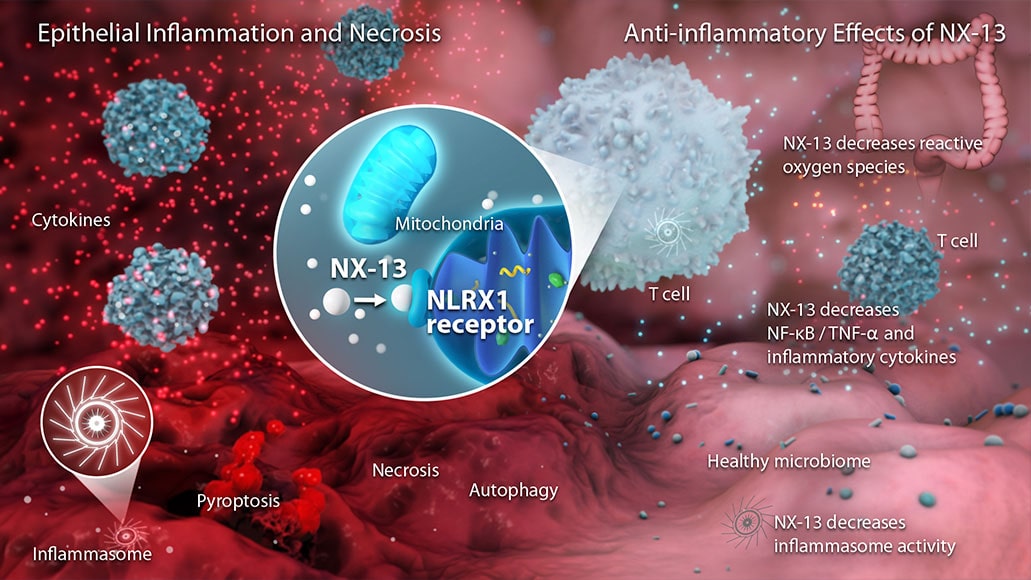
NX-13 is a potentially first-in-class novel, gut-selective, once-daily, oral therapeutic candidate that activates NLRX1 (NOD-like receptor X1), a mitochondria-associated receptor that has been associated with the modulation of inflammatory cytokines for UC.
In August 2022, the Company reported positive top-line results from a NX-13 Phase 1b trial, demonstrating a favorable safety and tolerability profile in UC patients across a range of once-daily doses. Results also indicated promising early signals of clinical improvement as soon as 2 weeks in patients’ symptoms and four weeks by endoscopy in exploratory endpoints.
In April 2023, we initiated the NEXUS, Phase 2 proof-of-concept trial to evaluate the safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics in patients with moderate to severe UC. The NEXUS trial is dose-ranging, blinded, placebo-controlled and statistically powered.
The Company plans to report topline results from the NEXUS trial in the fourth quarter of 2024.
*The NX-13 Phase 1b study was not powered for exploratory endpoints. Results are hypothesis generating only.